Read and Publish Agreements
What are Read and Publish Agreements?
UNE researchers have the opportunity to increase the reach of their work by publishing Open Access under several Read and Publish Agreements. UNE has signed up to Read and Publish Agreements with AIP Publishing, Cambridge University Press, CSIRO Publishing, Elsevier, Oxford University Press, Springer Nature, Taylor & Francis, and Wiley and Hindawi.
Read and Publish Agreements incorporate the Article Processing Charge (APC) into the institutional subscription fee payable to publishers. Institutions therefore pay a fee that covers access (reading) to research outputs, as well as the Open Access publishing cost (APC) for its authors in some of the journals in a publisher's portfolio. Read and Publish Agreements generally permit the authors of the articles to retain copyright, and the articles are published under one of the Creative Commons licences which enables flexible re-use and wider sharing of research. Articles published under these agreements are made Open Access in journals which operate under either the Gold or Hybrid models.
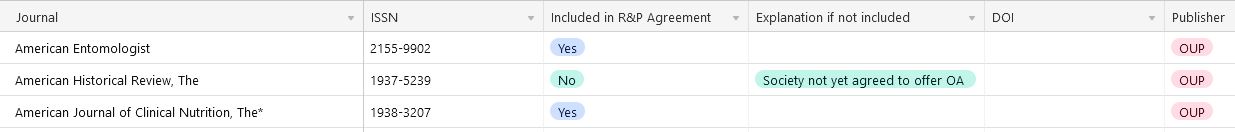
Authors wishing to publish their article as Open Access under the agreements must meet the following eligibility criteria: The journal you wish to publish in must be on the list of eligible titles under an agreement. Not all journals are included in the agreements. For example, Elsevier, AIP Publishing, Taylor & Francis, Springer Nature and Oxford University Press do not include fully Open Access (Gold) journals in the agreements. View the complete 2024 journal title list for UNE Spreadsheet last updated: 25 January 2024. The journal tool is an Excel spreadsheet which is a master file of all journal titles included in the eight Read and Publish Agreements at UNE. Please read the 'Read me tips' tab first. OR Refer to the individual summary pages for each Read and Publish Agreement Click on the summary pages for each Read and Publish Agreement to the left, and select the publisher of your choice. Then, once on the publisher agreement summary page, click on the green button titled 'Included journal titles'. The link takes you to an extended guide which provides greater detail about the agreements, including which journals are or are not included. Below is an example from the Oxford University Press journal list which shows 'The American Historical Review' is not included in the agreement. Eligibility criteria applies to the type of article that can be made Open Access under the agreements. For example, research articles, review articles, or case reports. The article types may be different across each agreement. Find out if the article type is eligible 1. Refer to the summary pages for each Read and Publish Agreement to the left, and select the publisher of your choice 2. Once on the publisher agreement summary page, click on the link 'view Eligible articles', next to the heading 'Eligible article type'. The link takes you to an extended guide which provides greater detail about the agreement, including which article types are eligible. Eligibility is tied to the article's corresponding author (or, responsible corresponding author for Wiley). The corresponding author needs to be affiliated with UNE at the time of the article's acceptance. IMPORTANT: Corresponding authors should use their institutional email address (@une.edu.au) when submitting an article. Using a personal email address may result in an article not being identified as eligible under the agreements. Eligibility to publish an article Open Access under the agreements attaches to the article's acceptance date, which must fall within the duration of an agreement term. If an article is submitted to a journal that is subject to article allowance limit (cap), the article will not be eligible for Open Access under the agreement if it is accepted after the cap expires. Article allowance limits run until the end of the calendar year, and reset on 1 January the following year. Please see the FAQ's below for more information.Eligibility criteria
Find out if a journal is included in an agreement
Article allowance limits (caps)
Article allowance limits, or caps refer to the maximum number of articles that can be accepted under an agreement in a calendar year. The caps are applied across all participating institutions in any given agreement, meaning individual participating institutions are not allocated a set number of articles that can be accepted in a calendar year. The cap is drawn down over the year on a ‘first come, first served’ basis across participating institutions.
Elsevier, Wiley and Hindawi, Springer Nature, Taylor & Francis, AIP Publishing and Oxford University Press have caps applied to their respective agreements.
CSIRO Publishing and Cambridge University Press on the other hand do not have caps, and will accept an unlimited number of eligible articles in a calendar year under the respective agreements.
Find out if a publisher's article allowance limit may be reached before the end of the calendar year
CAUL, the organisation responsible for negotiating Read and Publish agreements for the Australian tertiary sector provides updated data about article allowance limits. Please visit the CAUL Reports webpage for the latest data about the number of articles accepted under the agreements with caps, and whether the caps are predicted to be reached prior to the end of the calendar year.
Read and Publish agreements with Elsevier, Wiley and Hindawi, Taylor & Francis, AIP Publishing, Springer Nature and Oxford University Press have caps imposed on them. It is possible that prior to the end of the calendar year the total number of permitted articles across the consortia will be depleted. If this is the case, UNE authors can either: Authors publishing under the second option are encouraged to submit an accepted version of their article to RUNE, to be made Open Access via the Repository-based (green) Open Access pathway. UNE authors may still make their manuscript Open Access, irrespective of the Read and Publish agreements. If the eligible journal titles under the agreements are not relevant to an author’s research, or the journal is not an eligible journal, authors can still make their manuscript Open Access using RUNE, if publishing in journals that accept articles without charge e.g Hybrid or subscription journals. Repository-based (green) Open Access is a sustainable and supported path to Open Access and operates by authors depositing an accepted earlier version of their manuscript (that may otherwise be published behind a paywall) into an institutional or subject repository. In most cases, the author accepted manuscript version (post-print) can be made Open Access via UNE’s institutional repository, RUNE. The author accepted manuscript is the version that includes revisions based on reviewer’s feedback and comments but has not yet been copy-edited or typeset by the publisher.Frequently asked questions